问题描述
最近刚刚开始学习FEM,尝试使用课件中提到的Neo-Hookean模型复现弹簧形变,发现了两个问题:
-
当鼠标拖拽弹簧产生一定形变时,弹簧会骤然消失
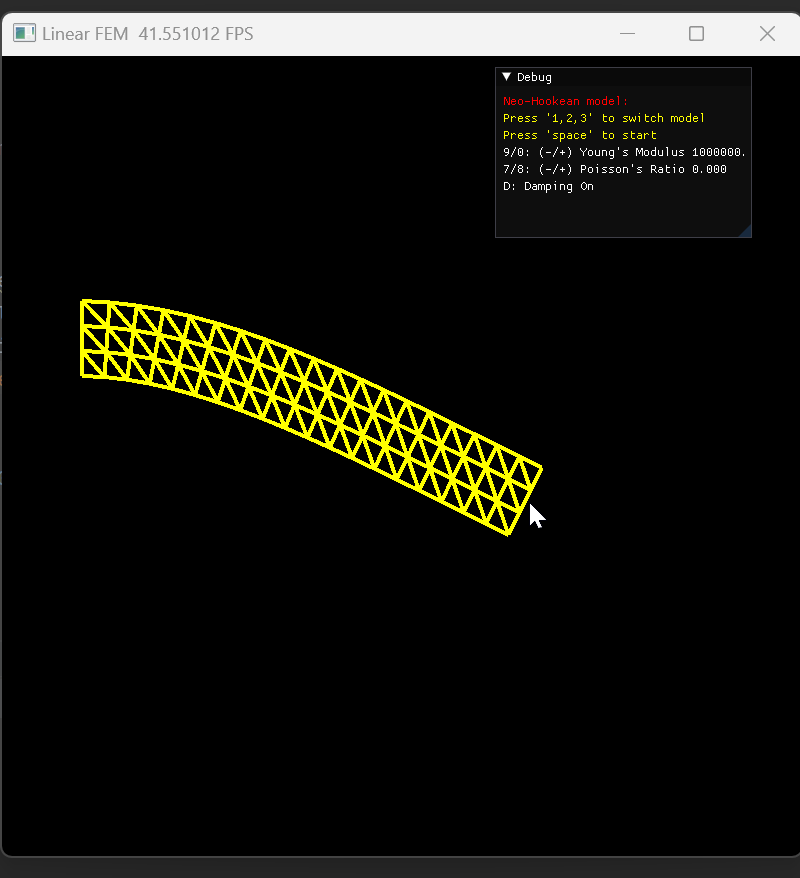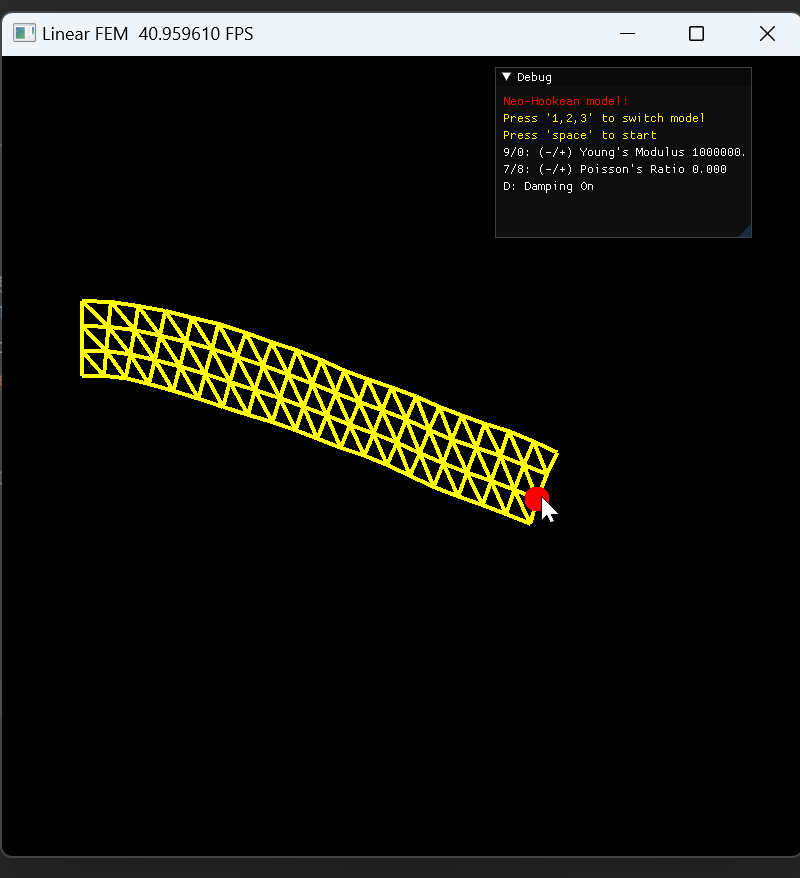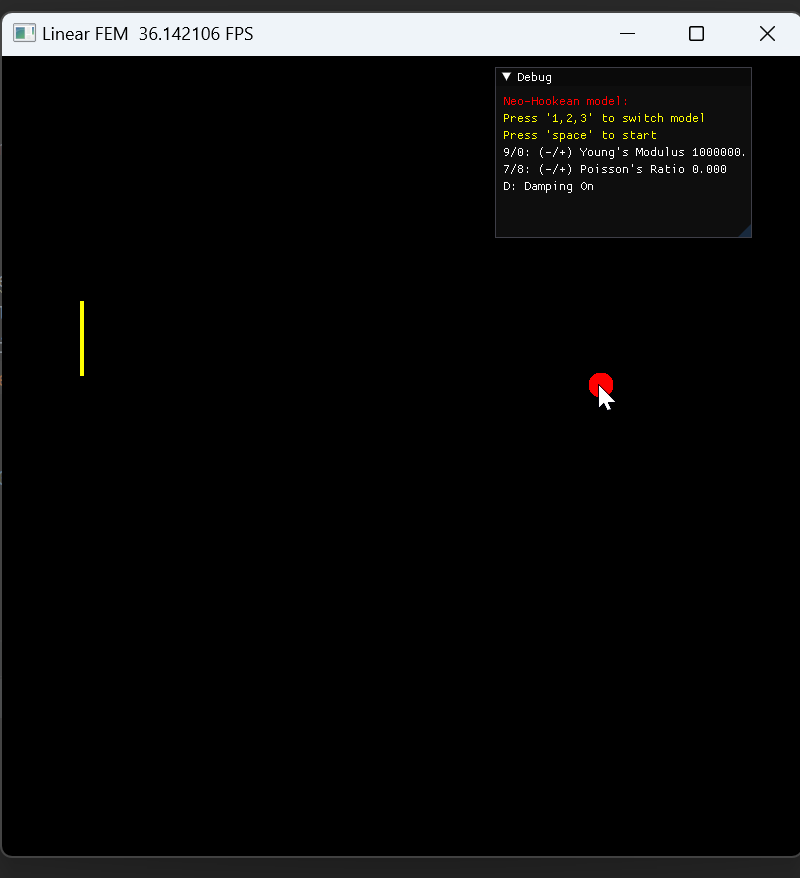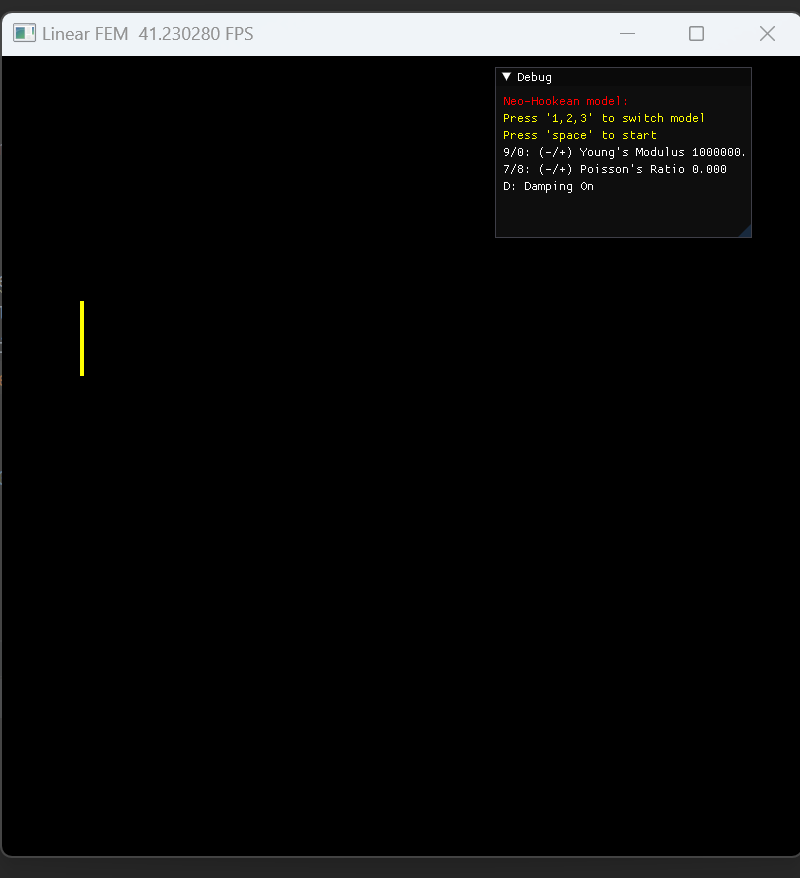
-
使用GGUI时无法侦测到键盘输入数字,如(1,2,3)
代码
import taichi as ti
import math
ti.init(arch=ti.gpu)
# global control
paused = True
# integration method
# 1: Co-rotated linear model
# 2: Venant Kirchhoff model ( StVK )
# 3: Neo-Hookean model
integration = 3
damping_toggle = ti.field(ti.i32, ())
curser = ti.Vector.field(2, ti.f64, ())
picking = ti.field(ti.i32, ())
using_auto_diff = False
# procedurally setting up the cantilever
init_x, init_y = 0.1, 0.6
N_x = 20
N_y = 4
# N_x = 2
# N_y = 2
N = N_x * N_y
N_edges = (N_x - 1) * N_y + N_x * (N_y - 1) + (N_x - 1) * \
(N_y - 1) # horizontal + vertical + diagonal springs
N_triangles = 2 * (N_x - 1) * (N_y - 1)
dx = 1 / 32
curser_radius = dx / 2
# physical quantities
m = 1
g = 9.8
YoungsModulus = ti.field(ti.f64, ())
PoissonsRatio = ti.field(ti.f64, ())
LameMu = ti.field(ti.f64, ())
LameLa = ti.field(ti.f64, ())
# time-step size (for simulation, 16.7ms)
h = 16.7e-3
# substepping
substepping = 100
# time-step size (for time integration)
dh = h / substepping
# simulation components
x = ti.Vector.field(2, ti.f64, N, needs_grad=True)
v = ti.Vector.field(2, ti.f64, N)
total_energy = ti.field(ti.f64, (), needs_grad=True)
grad = ti.Vector.field(2, ti.f64, N)
elements_Dm_inv = ti.Matrix.field(2, 2, ti.f64, N_triangles)
elements_V0 = ti.field(ti.f64, N_triangles)
# geometric components
triangles = ti.Vector.field(3, ti.i32, N_triangles)
edges = ti.Vector.field(2, ti.i32, N_edges)
@ti.func
def ij_2_index(i, j): return i * N_y + j
# -----------------------meshing and init----------------------------
@ti.kernel
def meshing():
# setting up triangles
for i, j in ti.ndrange(N_x - 1, N_y - 1):
# triangle id
tid = (i * (N_y - 1) + j) * 2
triangles[tid][0] = ij_2_index(i, j)
triangles[tid][1] = ij_2_index(i + 1, j)
triangles[tid][2] = ij_2_index(i, j + 1)
tid = (i * (N_y - 1) + j) * 2 + 1
triangles[tid][0] = ij_2_index(i, j + 1)
triangles[tid][1] = ij_2_index(i + 1, j + 1)
triangles[tid][2] = ij_2_index(i + 1, j)
# setting up edges
# edge id
eid_base = 0
# horizontal edges
for i in range(N_x - 1):
for j in range(N_y):
eid = eid_base + i * N_y + j
edges[eid] = [ij_2_index(i, j), ij_2_index(i + 1, j)]
eid_base += (N_x - 1) * N_y
# vertical edges
for i in range(N_x):
for j in range(N_y - 1):
eid = eid_base + i * (N_y - 1) + j
edges[eid] = [ij_2_index(i, j), ij_2_index(i, j + 1)]
eid_base += N_x * (N_y - 1)
# diagonal edges
for i in range(N_x - 1):
for j in range(N_y - 1):
eid = eid_base + i * (N_y - 1) + j
edges[eid] = [ij_2_index(i + 1, j), ij_2_index(i, j + 1)]
@ti.kernel
def initialize():
YoungsModulus[None] = 1e6
paused = True
# init position and velocity
for i, j in ti.ndrange(N_x, N_y):
index = ij_2_index(i, j)
x[index] = ti.Vector([init_x + i * dx, init_y + j * dx])
v[index] = ti.Vector([0.0, 0.0])
@ti.func
def compute_D(i):
a = triangles[i][0]
b = triangles[i][1]
c = triangles[i][2]
return ti.Matrix.cols([x[b] - x[a], x[c] - x[a]])
@ti.kernel
def initialize_elements():
for i in range(N_triangles):
Dm = compute_D(i)
elements_Dm_inv[i] = Dm.inverse()
elements_V0[i] = ti.abs(Dm.determinant()) / 2
# ----------------------core-----------------------------
@ti.func
def compute_R_2D(F):
R, S = ti.polar_decompose(F, ti.f64)
return R
@ti.func
def isnan(x):
nan = ti.math.isnan(x)
result = False
for i in range(len(nan)):
if nan[i]:
result = True
return result
@ti.kernel
def compute_gradient():
# clear gradient
for i in grad:
grad[i] = ti.Vector([0, 0])
# gradient of elastic potential
for i in range(N_triangles):
# F = Ds * Inv(Dm)
Ds = compute_D(i)
F = Ds @ elements_Dm_inv[i]
Eye = ti.Matrix.cols([[1.0, 0.0], [0.0, 1.0]])
if integration == 1:
# co-rotated linear elasticity
R = compute_R_2D(F)
# first Piola-Kirchhoff tensor
P = 2 * LameMu[None] * (F - R) + LameLa[None] * ((R.transpose()) @ F - Eye).trace() * R
# assemble to gradient
H = elements_V0[i] * P @ (elements_Dm_inv[i].transpose())
a, b, c = triangles[i][0], triangles[i][1], triangles[i][2]
gb = ti.Vector([H[0, 0], H[1, 0]])
gc = ti.Vector([H[0, 1], H[1, 1]])
ga = -gb - gc
grad[a] += ga
grad[b] += gb
grad[c] += gc
elif integration == 2:
# Venant-Kirchhoff model
Estvk = 0.5 * (F.transpose() @ F - Eye)
# first Piola-Kirchhoff tensor
P = F @ (2 * LameMu[None] * Estvk + LameLa[None] * Estvk.trace() * Eye)
# assemble to gradient
H = elements_V0[i] * P @ (elements_Dm_inv[i].transpose())
a, b, c = triangles[i][0], triangles[i][1], triangles[i][2]
gb = ti.Vector([H[0, 0], H[1, 0]])
gc = ti.Vector([H[0, 1], H[1, 1]])
ga = -gb - gc
grad[a] += ga
grad[b] += gb
grad[c] += gc
elif integration == 3:
J = max(F.determinant(), 1.)
# first Piola-Kirchhoff tensor
Fnt = F.inverse().transpose()
P = LameMu[None] * (F - Fnt) + LameLa[None] * ti.log(J) * Fnt
# assemble to gradient
H = elements_V0[i] * P @ (elements_Dm_inv[i].transpose())
a, b, c = triangles[i][0], triangles[i][1], triangles[i][2]
gb = ti.Vector([H[0, 0], H[1, 0]])
gc = ti.Vector([H[0, 1], H[1, 1]])
ga = -gb - gc
grad[a] += ga
grad[b] += gb
grad[c] += gc
@ti.kernel
def compute_total_energy():
for i in range(N_triangles):
Ds = compute_D(i)
F = Ds @ elements_Dm_inv[i]
Eye = ti.Matrix.cols([[1.0, 0.0], [0.0, 1.0]])
if integration == 1:
# co-rotated linear elasticity
R = compute_R_2D(F)
element_energy_density = LameMu[None] * ((F - R) @ (F - R).transpose()).trace() + 0.5 * LameLa[None] * (
R.transpose() @ F - Eye).trace() ** 2
total_energy[None] += element_energy_density * elements_V0[i]
elif integration == 2:
# Venant-Kirchhoff model
Estvk = 0.5 * (F.transpose() @ F - Eye)
element_energy_density = LameMu[None] * (Estvk @ Estvk.transpose()).trace() + 0.5 * LameLa[None] * (
Estvk).trace() ** 2
total_energy[None] += element_energy_density * elements_V0[i]
elif integration == 3:
J = F.determinant()
Jlog = ti.log(J)
d = 2
element_energy_density = 0.5 * LameMu[None] * ((J.transpose() @ J).trace() - d) + LameMu[
None] * Jlog + 0.5 * LameLa[None] * Jlog ** 2
total_energy[None] += element_energy_density * elements_V0[i]
@ti.kernel
def update():
# perform time integration
for i in range(N):
# symplectic integration
# elastic force + gravitation force, divding mass to get the acceleration
if using_auto_diff:
acc = -x.grad[i] / m - ti.Vector([0.0, g])
v[i] += dh * acc
else:
acc = -grad[i] / m - ti.Vector([0.0, g])
v[i] += dh * acc
x[i] += dh * v[i]
# explicit damping (ether drag)
for i in v:
if damping_toggle[None]:
v[i] *= ti.exp(-dh * 5)
# enforce boundary condition
for i in range(N):
if picking[None]:
r = x[i] - curser[None]
if r.norm() < curser_radius:
x[i] = curser[None]
v[i] = ti.Vector([0.0, 0.0])
pass
for j in range(N_y):
ind = ij_2_index(0, j)
v[ind] = ti.Vector([0, 0])
x[ind] = ti.Vector([init_x, init_y + j * dx]) # rest pose attached to the wall
for i in range(N):
if x[i][0] < init_x:
x[i][0] = init_x
v[i][0] = 0
@ti.kernel
def updateLameCoeff():
E = YoungsModulus[None]
nu = PoissonsRatio[None]
LameLa[None] = E * nu / ((1 + nu) * (1 - 2 * nu))
LameMu[None] = E / (2 * (1 + nu))
# init once and for all
meshing()
initialize()
initialize_elements()
updateLameCoeff()
# gui = ti.GUI('Linear FEM', (800, 800))
window = ti.ui.Window(name='Linear FEM', res=(800, 800), fps_limit=144)
canvas = window.get_canvas()
color = (0., 0., 0.)
canvas.set_background_color(color)
gui = window.get_gui()
point = ti.Vector.field(2, dtype=ti.f64, shape=1)
while window.running:
picking[None] = 0
# key events
for e in window.get_events(ti.ui.PRESS):
if e.key in [ti.ui.ESCAPE]:
exit()
elif e.key == '1':
integration = 1
elif e.key == '2':
integration = 2
elif e.key == '3':
integration = 3
elif e.key == 'r':
initialize()
elif e.key == '0':
YoungsModulus[None] *= 1.1
elif e.key == '9':
YoungsModulus[None] /= 1.1
if YoungsModulus[None] <= 0:
YoungsModulus[None] = 0
elif e.key == '8':
PoissonsRatio[None] = PoissonsRatio[None] * 0.9 + 0.05 # slowly converge to 0.5
if PoissonsRatio[None] >= 0.499:
PoissonsRatio[None] = 0.499
elif e.key == '7':
PoissonsRatio[None] = PoissonsRatio[None] * 1.1 - 0.05
if PoissonsRatio[None] <= 0:
PoissonsRatio[None] = 0
elif e.key == ti.GUI.SPACE:
paused = not paused
elif e.key == 'd' or e.key == 'D':
damping_toggle[None] = not damping_toggle[None]
elif e.key == 'p' or e.key == 'P': # step-forward
for i in range(substepping):
if using_auto_diff:
total_energy[None] = 0
with ti.Tape(total_energy):
compute_total_energy()
else:
compute_gradient()
update()
updateLameCoeff()
if window.is_pressed(ti.ui.LMB):
curser[None] = window.get_cursor_pos()
picking[None] = 1
# numerical time integration
if not paused:
for i in range(substepping):
if using_auto_diff:
total_energy[None] = 0
with ti.Tape(total_energy):
compute_total_energy()
else:
compute_gradient()
update()
# render
# pos = x.to_numpy()
# for i in range(N_edges):
# a, b = edges[i][0], edges[i][1]
# gui.line((pos[a][0], pos[a][1]),
# (pos[b][0], pos[b][1]),
# radius=1,
# color=(1.,1.,0))
# gui.line((init_x, 0.0), (init_x, 1.0), color=0xFFFFFF, radius=4)
canvas.lines(x, 0.005, indices=edges, color=(1., 1., 0.))
if picking[None]:
# gui.circle((curser[None][0], curser[None][1]), radius=curser_radius*800, color=0xFF8888)
point[0] = ti.Vector(curser.to_numpy().tolist())
canvas.circles(point, radius=curser_radius, color=(1.0, 0.0, 0.0))
# text
if integration == 1:
gui.text(f'Co-rotated linear model: ', color=(1., 0, 0))
elif integration == 2:
gui.text(f'Venant-Kirchhoff model: ', color=(1., 0, 0))
else:
gui.text(f'Neo-Hookean model: ', color=(1., 0, 0))
gui.text(f'Press \'1,2,3\' to switch model', color=(1., 1., 0))
gui.text(f'Press \'space\' to start', color=(1., 1., 0))
gui.text(
f'9/0: (-/+) Young\'s Modulus {YoungsModulus[None]:.1f}', color=(1., 1., 1.))
gui.text(
f'7/8: (-/+) Poisson\'s Ratio {PoissonsRatio[None]:.3f}', color=(1., 1., 1.))
if damping_toggle[None]:
gui.text(
'D: Damping On', color=(1., 1., 1.))
else:
gui.text(
'D: Damping Off', color=(1., 1., 1.))
window.show()
运行环境
[Taichi] version 1.7.1, llvm 15.0.1, commit 0f143b2f, win, python 3.9.19
[Taichi] Starting on arch=cuda