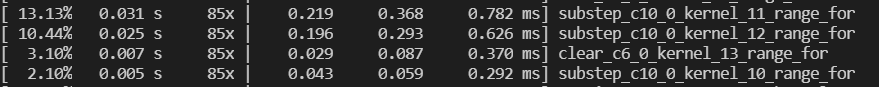试了一下重写一个TressFX实时毛发模拟
TressFX 也是多年前的方法了,不过直到今天也少有游戏使用发丝物理模拟
Han, Dongsoo, and Takahiro Harada. “Real-time hair simulation with efficient hair style preservation.” (2012).

并没有完全重写tressfx所有pass,只实现了global local constraint和length constraint
一个性能对比,在6720根毛发,每根32段下,
官方DX12 Compute Demo里,Integrate, Global, Local constraint 大约0.7ms
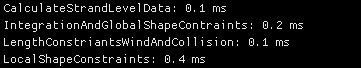
Taichi里这几个pass加起来也差不多0.7ms
性能差不多在同一个数量级,考虑到我也没啥优化经验就能做到这样,而官方Demo里computer shader的编写难度较高,要大量使用groupshare memory,确实写taichi还是容易不少的。
# TressFX with taichi
# author: info@ma-yidong.com
# some code adopted from https://github.com/lyd405121/OpenClothPy
import taichi as ti
ti.init(arch=ti.gpu, kernel_profiler=True)
steps = 1
# strand params
n_strand = 100
n_strand_split = 32
stiffness_local = 0.9
stiffness_global = 0.005
# global buffer
transform_root = ti.Matrix.field(4,4, float, n_strand)
pos = ti.Vector.field(3, float, (n_strand, n_strand_split))
pos_prev = ti.Vector.field(3, float, (n_strand, n_strand_split))
pos_rest = ti.Vector.field(3, float, (n_strand, n_strand_split))
length_rest = ti.Vector.field(1, float, (n_strand, n_strand_split))
time_elapsed = ti.field(float, (1))
# other params
imgSize = 720
img = ti.Vector.field(3, float, shape=[imgSize,imgSize])
screenRes = ti.Vector([imgSize, imgSize])
gravity = ti.Vector([0.0, -9.8, 0.0])
deltaT = 0.0167
@ti.func
def get_length2(v):
return ti.sqrt(v.x*v.x+ v.y*v.y)
@ti.func
def quat_normalize(q):
n = q.dot(q)
if n < 1e-10:
q.w = 1.0
else:
q *= 1.0 / ti.sqrt(n)
return q
@ti.func
def quat_from_two_unit_vector(u, v):
r = 1.0 + u.dot(v)
n = ti.Vector([0.0,0.0,0.0])
if r < 1e-7:
r = 0.0
if ti.abs(u.x) > ti.abs(u.z):
n = ti.Vector([-u[1], u[0], 0.0])
else:
n = ti.Vector([0.0, -u[2], u[1]])
else:
n = u.cross(v)
q = ti.Vector([n[0], n[1], n[2], r])
return quat_normalize(q)
@ti.func
def mul_quat_and_vector(q, v):
qvec = ti.Vector([q[0], q[1], q[2]])
uv = qvec.cross(v)
uuv = qvec.cross(uv)
uv *= (2.0 * q[3])
uuv *= 2.0
return v + uv + uuv
@ti.func
def make_matrix_rotation_x(angle):
return ti.Matrix([
[1,0,0,0],
[0,ti.cos(angle),ti.sin(angle),0],
[0,-ti.sin(angle),ti.cos(angle),0],
[0,0,0,1]])
@ti.func
def make_matrix_translation(translation):
return ti.Matrix([
[1,0,0,translation.x],
[0,1,0,translation.y],
[0,0,1,translation.z],
[0,0,0,1]])
@ti.func
def make_homogeneous(vec):
return ti.Vector([vec.x, vec.y, vec.z, 1])
@ti.func
def make_3d(vec):
return ti.Vector([vec.x, vec.y, vec.z])
@ti.func
def fill_pixel(v, z, c):
if (v.x >= 0) and (v.x <screenRes.x) and (v.y >=0 ) and (v.y < screenRes.y):
img[v] = c
@ti.func
def transform(vec):
phi, theta = 90 * 3.14 / 180.0, 32 * 3.14 / 180.0
vec = vec * 0.1
x, y, z = vec.x-0.2, vec.y-0.3, vec.z
c, s = ti.cos(phi), ti.sin(phi)
C, S = ti.cos(theta), ti.sin(theta)
x, z = x * c + z * s, z * c - x * s
u, v = x, y * C + z * S
return ti.Vector([(u+0.5)* imgSize,(v+0.5)* imgSize, 0.5])
#https://github.com/miloyip/line/blob/master/line_bresenham.c can be further optimized
@ti.func
def draw_line(v0,v1):
v0 = transform(v0)
v1 = transform(v1)
s0 = ti.Vector([ti.cast(v0.x, ti.i32), ti.cast(v0.y, ti.i32)])
s1 = ti.Vector([ti.cast(v1.x, ti.i32), ti.cast(v1.y, ti.i32)])
dis = get_length2(s1 - s0)
x0 = s0.x
y0 = s0.y
z0 = v0.z
x1 = s1.x
y1 = s1.y
z1 = v1.z
dx = abs(x1 - x0)
sx = -1
if x0 < x1 :
sx = 1
dy = abs(y1 - y0)
sy = -1
if y1 > y0:
sy = 1
dz = z1 - z0
err = 0
if dx > dy :
err = ti.cast(dx/2, ti.i32)
else :
err = ti.cast(-dy/2, ti.i32)
for i in range(0, 64):
distC = get_length2( ti.Vector([x1,y1])- ti.Vector([x0,y0]))
fill_pixel(ti.Vector([x0,y0]), dz * (distC / dis) + v0.z, ti.Vector([0.64, 0.804, 0.902]))
e2 = err
if (e2 > -dx):
err -= dy
x0 += sx
if (e2 < dy):
err += dx
y0 += sy
if (x0 == x1) and (y0 == y1):
break
@ti.kernel
def draw():
for i,j in pos:
if j < n_strand_split-1:
draw_line(pos[i,j], pos[i,j+1])
@ti.kernel
def clear():
for i, j in img:
img[i,j] = ti.Vector([0.06,0.184,0.255])
@ti.kernel
def drive_root():
time_elapsed[0] += deltaT * 0.3
center = ti.Vector([0,6,0])
frac = ti.abs(time_elapsed[0] - ti.floor(time_elapsed[0]))
frac = ti.sin(frac * 2 * 3.1415)
frac *= 0.2
for i in range(n_strand):
mat = make_matrix_translation(-center) @ make_matrix_rotation_x(frac) @ make_matrix_translation(center)
transform_root[i] = mat
@ti.kernel
def substep():
for i,j in pos:
coord = ti.Vector([i, j])
rest = pos_rest[coord]
# apply skinning
initial_pos = transform_root[i] @ ti.Vector([rest.x, rest.y, rest.z, 1])
# gravity and integrate
if j > 0:
acc = gravity
tmp = pos[coord]
pos[coord] = (2*pos[coord] - pos_prev[coord]) + acc * deltaT * deltaT
pos_prev[coord] = tmp
else: # root
pos[coord] = ti.Vector([initial_pos.x, initial_pos.y, initial_pos.z])
# global shape constraints
pos[coord] += stiffness_global * ( ti.Vector([initial_pos.x, initial_pos.y, initial_pos.z]) - pos[coord])
# local shape constraints
for i in range(n_strand):
bone_mat = transform_root[i]
for j in range(1, n_strand_split-1):
bind_pos = make_3d(bone_mat @ make_homogeneous(pos_rest[i,j]))
bind_pos_before = make_3d(bone_mat @ make_homogeneous(pos_rest[i,j-1]))
bind_pos_after = make_3d(bone_mat @ make_homogeneous(pos_rest[i,j+1]))
vec_bind = bind_pos_after - bind_pos
vec_prv_bind = bind_pos - bind_pos_before
last_vec = pos_rest[i,j] - pos_rest[i,j-1]
rot_global = quat_from_two_unit_vector(vec_prv_bind.normalized(), last_vec.normalized())
orgPos_i_plus_1_InGlobalFrame = mul_quat_and_vector(rot_global, vec_prv_bind) + pos[i,j]
dist = stiffness_global * (orgPos_i_plus_1_InGlobalFrame - pos[i,j+1])
pos[i,j] -= dist
pos[i,j+1] += dist
# edge length constraint
for it in ti.static(range(1)):
for i in range(n_strand):
for j in range(0, n_strand_split-1):
delta = pos[i, j+1] - pos[i,j]
stretch = 1.0 - length_rest[i,j][0] / delta.norm()
delta *= stretch
if j == 0:
pos[i,j+1] -= delta
else:
pos[i,j] += delta * 0.5
pos[i,j+1] -= delta * 0.5
# collision to add
@ti.kernel
def init():
# precompute rest-state values
strand_seg_len = 5.0 / n_strand_split
for i in range(n_strand):
base_pos = ti.Vector([ti.random() * 0.2, 5.0, ti.random() * 0.2])
for j in range(n_strand_split):
phase_offset = ti.random() * 5
local_offset = ti.Vector([
j * base_pos.x * 0.2 + j * 0.02 * ti.cos(phase_offset + j/0.5),
-j * strand_seg_len,
j * base_pos.z * 0.2 + j * 0.02 * ti.sin(phase_offset + j/0.5)])
pos[i, j] = base_pos + local_offset
pos_prev [i, j] = pos[i, j]
pos_rest[i, j] = pos[i, j]
length_rest[i,j] = ti.Vector([strand_seg_len])
init()
gui = ti.GUI('TressFx Demo', res=(imgSize,imgSize))
while gui.running and not gui.get_event(gui.ESCAPE):
drive_root()
for s in range(steps):
substep()
clear()
draw()
gui.set_image(img.to_numpy())
gui.show()
ti.kernel_profiler_print()