import numpy as np
import math
import random
ti.init(arch=ti.gpu)
nx = 800
ny = 400
pixels = ti.Vector(3, dt=ti.f32, shape=(nx, ny))
FOV = 90
APERTURE = 0.1
def normalize(n):
s = 1.0 / math.sqrt(np.dot(n, n))
return n * s
lookfrom = np.array([6.5, 1.5, 2.0], dtype=np.float32)
lookat = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=np.float32)
up = np.array([0.0, 1.0, 0.0], dtype=np.float32)
view_dir = lookfrom - lookat
lens_radius = APERTURE / 2
dist_to_focus = np.sqrt((view_dir * view_dir).sum())
w = normalize(view_dir)
u = normalize(np.cross(up, w))
v = np.cross(w, u)
aspect = ny / nx
fov_theta = FOV * math.pi / 180
half_width = math.tan(fov_theta / 2)
half_height = half_width * aspect
origin = ti.Vector(lookfrom)
lower_left_corner = ti.Vector(lookfrom - (half_width * u + half_height * v + w) * dist_to_focus)
horizontal = ti.Vector(u * 2 * half_width) * dist_to_focus
vertical = ti.Vector(v * 2 * half_height) * dist_to_focus
SIZEN = 20
def r():
return random.random()
# 0-2代表球心,3代表半径, 4代表类型(0漫反射,1镜面反射, 2折射), 5-7代表材质颜色
# 对于折射 4代表折射率
spheres = ti.Vector(8, dt=ti.f32, shape=SIZEN)
spheres[0] = np.array([0.0, -1000.0, 0.0, 1000.0, 0.0, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5], dtype=np.float32)
spheres[1] = np.array([0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 1.5, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=np.float32)
spheres[2] = np.array([-4.0, 1.0,-0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.4, 0.2, 0.1], dtype=np.float32)
spheres[3] = np.array([4.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.7, 0.6, 0.5], dtype=np.float32)
k = 4
for i in range(-10, 10, 6):
for j in range(-10, 10, 6):
center = np.array([i + 0.9 * random.random(), 0.5, j + 0.9 * random.random()], dtype = np.float32)
choose = random.random()
if choose < 0.4:
spheres[k] = np.array([ center[0], center[1], center[2], 0.5, 0.0, r() * r(), r() * r(), r() * r()] , dtype = np.float32)
elif choose < 0.7:
spheres[k] = np.array([ center[0], center[1], center[2], 0.5, 1.0, 0.5 * (1 + r()), 0.5 * (1 + r()), 0.5 * (1 + r())] , dtype = np.float32)
else:
spheres[k] = np.array([ center[0], center[1], center[2], 0.5, 2.0, 1.5, 0, 0] , dtype = np.float32)
k += 1
# spheres[4] = np.array([-1.0, 0.0, -1.0, -0.45, 2.0, 1.5, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=np.float32)
@ti.func
def unit_vector(v):
k = 1 / (ti.sqrt(v.dot(v)))
return k * v
#镜面反射
@ti.func
def reflect(v, n):
return v - 2 * v.dot(n) * n
#折射
@ti.func
def refract(v, n, ni_over_nt):
dt = v.dot(n)
#小于0时是全反射
discriminant = 1.0 - ni_over_nt * ni_over_nt * ( 1.0 - dt * dt)
succ = False
refracted = ti.Vector([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
if discriminant > 0:
refracted = ni_over_nt * (v - n * dt) - n * ti.sqrt(discriminant)
succ = True
return succ, refracted
@ti.func
def schlick(cosine, ref_idx):
r0 = (1.0 - ref_idx) / (1 + ref_idx)
r0 = r0 * r0
return r0 + (1 - r0) * ti.pow((1- cosine), 5)
# http://www.pbr-book.org/3ed-2018/Monte_Carlo_Integration/2D_Sampling_with_Multidimensional_Transformations.html
@ti.func
def random_in_unit_sphere():
eta1 = ti.random()
eta2 = ti.random()
coeff = 2 * ti.sqrt(eta1 * (1 - eta1))
eta2m2pi = eta2 * math.pi * 2
return ti.Vector([ti.cos(eta2m2pi) * coeff, ti.sin(eta2m2pi) * coeff, 1 - 2 * eta1])
@ti.func
def random_in_unit_disk():
eta1 = ti.random()
eta2 = ti.random()
r = ti.sqrt(eta1)
theta = math.pi * 2 * eta2
return ti.Vector([r * ti.cos(theta), r * ti.sin(theta)])
@ti.func
def hit_sphere(center, radius, rayo, rayd, mint, maxt):
rst = False
t = 0.0
oc = rayo - center
a = rayd.dot(rayd)
b = 2.0 * oc.dot(rayd)
c = oc.dot(oc) - radius * radius
disc = b * b - 4.0 * a * c
if disc >= 0:
sq = ti.sqrt(disc)
t = (-b - sq) / (2.0 * a)
if t > mint and t < maxt:
rst = True
else:
t = (-b + sq) / (2.0 * a)
if t > mint and t < maxt:
rst = True
return rst, t, rayo + t * rayd
@ti.func
def hit_spheres(rayo, rayd, mint, maxt):
rst = False
rt = 1e10
p = ti.Vector([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
normal = ti.Vector([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
index = -1
for i in ti.static(range(SIZEN)):
sc = ti.Vector([spheres[i][0], spheres[i][1], spheres[i][2]])
r = spheres[i][3]
hit, t, hitp = hit_sphere(sc, r, rayo, rayd, mint, maxt)
if hit and t < rt:
rst = True
rt = t
normal = unit_vector(hitp - sc)
p = hitp
index = i
#是否命中, 命中点, 命中点法线, 命中球体索引
return rst, p, normal, index
@ti.func
def color(o, d):
rst = ti.Vector([1.0, 1.0, 1.0])
count = 0
while True:
if count > 10:
break
hit, p, n, index = hit_spheres(o, d, 0.001, 1e10)
if hit:
#命中点是下一条光线的起点
o = p
if spheres[index][4] <= 1.0:
albedo = ti.Vector([spheres[index][5], spheres[index][6], spheres[index][7]])
rst = rst * albedo
#漫反射
if spheres[index][4] == 0.0:
d = unit_vector(n + random_in_unit_sphere())
#镜面反射
elif spheres[index][4] == 1.0:
# d = unit_vector(reflect(d, n) + random_in_unit_sphere() * 0.03)
d = reflect(d, n)
if n.dot(d) < 0:
rst = ti.Vector([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
break
#折射
else:
outward_n = n
#折射率比值
ni_over_nt = spheres[index][5]
cosine = 0.0
#从球体内部往外部
if (d.dot(n)) > 0:
outward_n = -n
cosine = ni_over_nt * d.dot(n)
#从球体外部到内部
else:
ni_over_nt = 1.0 / ni_over_nt
cosine = -d.dot(n)
succ, refracted = refract(d, outward_n, ni_over_nt)
if succ:
#一定概率折射或者反射
reflect_prob = schlick(cosine, spheres[index][5])
if ti.random() < reflect_prob:
d = reflect(d, n)
else:
d = refracted
#完全反射
else:
d = reflect(d, n)
count += 1
else:
t = 0.5 * (d[1] + 1.0)
skycolor = (1.0 - t) * ti.Vector([1.0, 1.0, 1.0]) + t * ti.Vector([0.5, 0.7, 1.0])
rst = rst * skycolor
break
return rst
@ti.kernel
def paint():
for i, j in pixels:
col = ti.Vector([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
# 每像素点采样次数
for _ in ti.static(range(4)):
uu = (float(i) + ti.random()) / float(nx)
vv = (float(j) + ti.random()) / float(ny)
rd = lens_radius * random_in_unit_disk()
offset = uu * rd[0] + vv * rd[1]
direction = lower_left_corner + uu * horizontal + vv * vertical - origin - offset
col += color(origin + offset, unit_vector(direction))
pixels[i, j] = col * 0.25
gui = ti.GUI("Ray12", (nx, ny))
for i in range(1000):
paint()
gui.set_image(pixels.to_numpy())
gui.show()
开头少一句 import taichi as ti
补个图
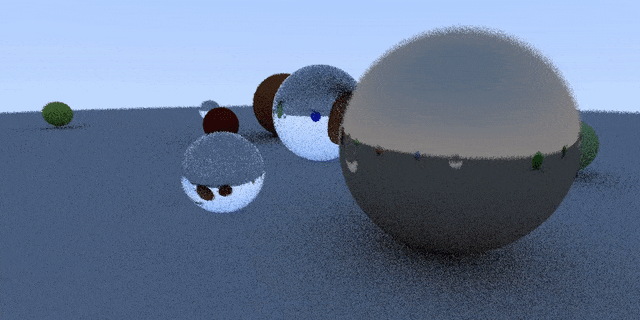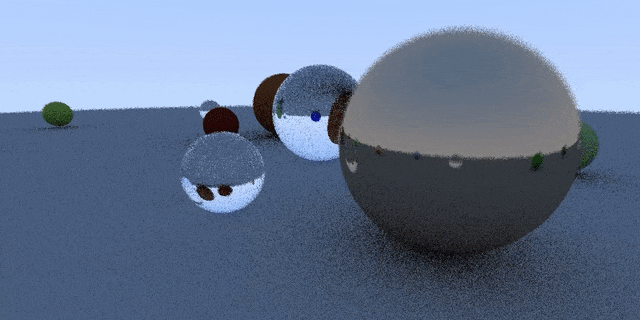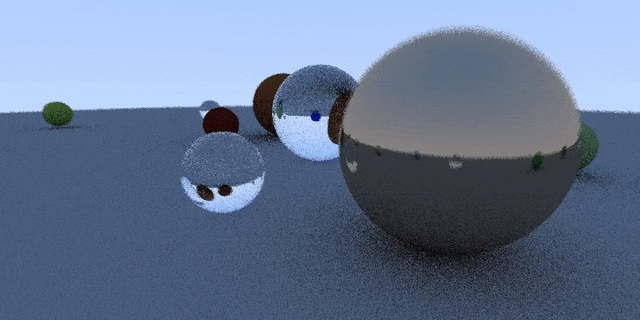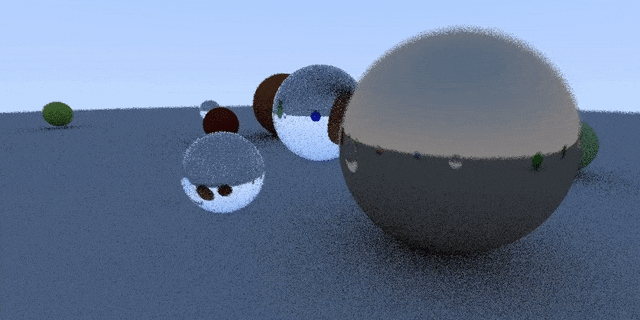
我是用的是taichi 0.6.9, 发现第39行 “horizontal = ti.Vector(u * 2 * half_width) * dist_to_focus” 报错了.
[Taichi] mode=release
[Taichi] version 0.6.9, supported archs: [cpu, cuda, opengl], commit afd6650c, python 3.7.6
Traceback (most recent call last):
File “ray_tracer.py”, line 39, in
horizontal = ti.Vector(u * 2 * half_width) * dist_to_focus
File “/home/sai/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/taichi/lang/common_ops.py”, line 55, in mul
return ti.mul(self, other)
File “/home/sai/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/taichi/lang/ops.py”, line 56, in wrapped
return a.element_wise_binary(imp_foo, b)
File “/home/sai/anaconda3/lib/python3.7/site-packages/taichi/lang/util.py”, line 196, in wrapped
f’{func.name} cannot be called in Python-scope’
AssertionError: element_wise_binary cannot be called in Python-scope
乘法放到里面去就行了
horizontal = ti.Vector(u * 2 * half_width * dist_to_focus)
vertical = ti.Vector(v * 2 * half_height * dist_to_focus)
对的, 我就是把这个放到kernel里面去了.
修正版:
import taichi as ti
import numpy as np
import math
import random
ti.init(arch=ti.gpu)
nx = 800
ny = 400
pixels = ti.Vector(3, dt=ti.f32, shape=(nx, ny))
FOV = 90
APERTURE = 0.1
def normalize(n):
s = 1.0 / math.sqrt(np.dot(n, n))
return n * s
lookfrom = np.array([6.5, 1.5, 2.0], dtype=np.float32)
lookat = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=np.float32)
up = np.array([0.0, 1.0, 0.0], dtype=np.float32)
view_dir = lookfrom - lookat
lens_radius = APERTURE / 2
dist_to_focus = np.sqrt((view_dir * view_dir).sum())
w = normalize(view_dir)
u = normalize(np.cross(up, w))
v = np.cross(w, u)
aspect = ny / nx
fov_theta = FOV * math.pi / 180
half_width = math.tan(fov_theta / 2)
half_height = half_width * aspect
origin = lookfrom
lower_left_corner = lookfrom - (half_width * u + half_height * v + w) * dist_to_focus
horizontal = u * 2 * half_width * dist_to_focus
vertical = v * 2 * half_height * dist_to_focus
SIZEN = 20
def r():
return random.random()
# 0-2代表球心,3代表半径, 4代表类型(0漫反射,1镜面反射, 2折射), 5-7代表材质颜色
# 对于折射 4代表折射率
spheres = ti.Vector(8, dt=ti.f32, shape=SIZEN)
spheres[0] = np.array([0.0, -1000.0, 0.0, 1000.0, 0.0, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5], dtype=np.float32)
spheres[1] = np.array([0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 2.0, 1.5, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=np.float32)
spheres[2] = np.array([-4.0, 1.0,-0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.4, 0.2, 0.1], dtype=np.float32)
spheres[3] = np.array([4.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.7, 0.6, 0.5], dtype=np.float32)
k = 4
for i in range(-10, 10, 6):
for j in range(-10, 10, 6):
center = np.array([i + 0.9 * random.random(), 0.5, j + 0.9 * random.random()], dtype = np.float32)
choose = random.random()
if choose < 0.4:
spheres[k] = np.array([ center[0], center[1], center[2], 0.5, 0.0, r() * r(), r() * r(), r() * r()] , dtype = np.float32)
elif choose < 0.7:
spheres[k] = np.array([ center[0], center[1], center[2], 0.5, 1.0, 0.5 * (1 + r()), 0.5 * (1 + r()), 0.5 * (1 + r())] , dtype = np.float32)
else:
spheres[k] = np.array([ center[0], center[1], center[2], 0.5, 2.0, 1.5, 0, 0] , dtype = np.float32)
k += 1
# spheres[4] = np.array([-1.0, 0.0, -1.0, -0.45, 2.0, 1.5, 0.0, 0.0], dtype=np.float32)
@ti.func
def unit_vector(v):
k = 1 / (ti.sqrt(v.dot(v)))
return k * v
#镜面反射
@ti.func
def reflect(v, n):
return v - 2 * v.dot(n) * n
#折射
@ti.func
def refract(v, n, ni_over_nt):
dt = v.dot(n)
#小于0时是全反射
discriminant = 1.0 - ni_over_nt * ni_over_nt * ( 1.0 - dt * dt)
succ = False
refracted = ti.Vector([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
if discriminant > 0:
refracted = ni_over_nt * (v - n * dt) - n * ti.sqrt(discriminant)
succ = True
return succ, refracted
@ti.func
def schlick(cosine, ref_idx):
r0 = (1.0 - ref_idx) / (1 + ref_idx)
r0 = r0 * r0
return r0 + (1 - r0) * ti.pow((1- cosine), 5)
# http://www.pbr-book.org/3ed-2018/Monte_Carlo_Integration/2D_Sampling_with_Multidimensional_Transformations.html
@ti.func
def random_in_unit_sphere():
eta1 = ti.random()
eta2 = ti.random()
coeff = 2 * ti.sqrt(eta1 * (1 - eta1))
eta2m2pi = eta2 * math.pi * 2
return ti.Vector([ti.cos(eta2m2pi) * coeff, ti.sin(eta2m2pi) * coeff, 1 - 2 * eta1])
@ti.func
def random_in_unit_disk():
eta1 = ti.random()
eta2 = ti.random()
r = ti.sqrt(eta1)
theta = math.pi * 2 * eta2
return ti.Vector([r * ti.cos(theta), r * ti.sin(theta)])
@ti.func
def hit_sphere(center, radius, rayo, rayd, mint, maxt):
rst = False
t = 0.0
oc = rayo - center
a = rayd.dot(rayd)
b = 2.0 * oc.dot(rayd)
c = oc.dot(oc) - radius * radius
disc = b * b - 4.0 * a * c
if disc >= 0:
sq = ti.sqrt(disc)
t = (-b - sq) / (2.0 * a)
if t > mint and t < maxt:
rst = True
else:
t = (-b + sq) / (2.0 * a)
if t > mint and t < maxt:
rst = True
return rst, t, rayo + t * rayd
@ti.func
def hit_spheres(rayo, rayd, mint, maxt):
rst = False
rt = 1e10
p = ti.Vector([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
normal = ti.Vector([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
index = -1
for i in ti.static(range(SIZEN)):
sc = ti.Vector([spheres[i][0], spheres[i][1], spheres[i][2]])
r = spheres[i][3]
hit, t, hitp = hit_sphere(sc, r, rayo, rayd, mint, maxt)
if hit and t < rt:
rst = True
rt = t
normal = unit_vector(hitp - sc)
p = hitp
index = i
#是否命中, 命中点, 命中点法线, 命中球体索引
return rst, p, normal, index
@ti.func
def color(o, d):
rst = ti.Vector([1.0, 1.0, 1.0])
count = 0
while True:
if count > 10:
break
hit, p, n, index = hit_spheres(o, d, 0.001, 1e10)
if hit:
#命中点是下一条光线的起点
o = p
if spheres[index][4] <= 1.0:
albedo = ti.Vector([spheres[index][5], spheres[index][6], spheres[index][7]])
rst = rst * albedo
#漫反射
if spheres[index][4] == 0.0:
d = unit_vector(n + random_in_unit_sphere())
#镜面反射
elif spheres[index][4] == 1.0:
# d = unit_vector(reflect(d, n) + random_in_unit_sphere() * 0.03)
d = reflect(d, n)
if n.dot(d) < 0:
rst = ti.Vector([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
break
#折射
else:
outward_n = n
#折射率比值
ni_over_nt = spheres[index][5]
cosine = 0.0
#从球体内部往外部
if (d.dot(n)) > 0:
outward_n = -n
cosine = ni_over_nt * d.dot(n)
#从球体外部到内部
else:
ni_over_nt = 1.0 / ni_over_nt
cosine = -d.dot(n)
succ, refracted = refract(d, outward_n, ni_over_nt)
if succ:
#一定概率折射或者反射
reflect_prob = schlick(cosine, spheres[index][5])
if ti.random() < reflect_prob:
d = reflect(d, n)
else:
d = refracted
#完全反射
else:
d = reflect(d, n)
count += 1
else:
t = 0.5 * (d[1] + 1.0)
skycolor = (1.0 - t) * ti.Vector([1.0, 1.0, 1.0]) + t * ti.Vector([0.5, 0.7, 1.0])
rst = rst * skycolor
break
return rst
@ti.kernel
def paint():
for i, j in pixels:
col = ti.Vector([0.0, 0.0, 0.0])
# 每像素点采样次数
for _ in ti.static(range(4)):
uu = (float(i) + ti.random()) / float(nx)
vv = (float(j) + ti.random()) / float(ny)
rd = lens_radius * random_in_unit_disk()
offset = uu * rd[0] + vv * rd[1]
direction = ti.Vector(lower_left_corner) + uu * ti.Vector(horizontal) + vv * ti.Vector(vertical) - ti.Vector(origin) - offset
col += color(ti.Vector(origin) + offset, unit_vector(direction))
pixels[i, j] = col * 0.25
gui = ti.GUI("Ray12", (nx, ny))
for i in range(1000):
paint()
gui.set_image(pixels.to_numpy())
gui.show()