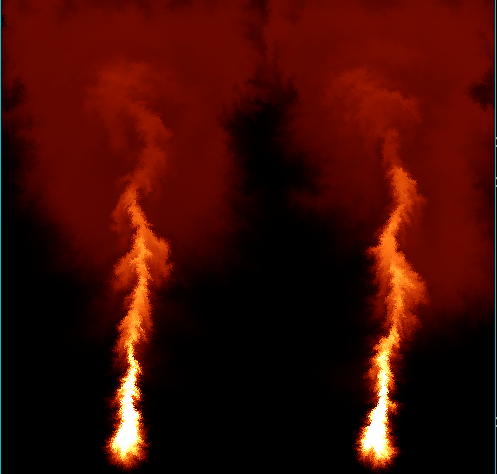
试着写了个流体的solver哈哈 ![]()
![]()
代码:
import taichi as ti
import numpy as np
import time
res = 500
dx = 1.0
dt = 0.03
inv_dx = 1.0 / dx
half_inv_dx = 0.5 * inv_dx
p_jacobi_iters = 20
density_decay = 0.99
vorticity = 10.0
ti.init(arch=ti.gpu)
_velocities = ti.Vector(2, dt=ti.f32, shape=(res, res))
_new_velocities = ti.Vector(2, dt=ti.f32, shape=(res, res))
velocity_divs = ti.var(dt=ti.f32, shape=(res, res))
velocity_curl = ti.var(dt=ti.f32, shape=(res, res))
_pressures = ti.var(dt=ti.f32, shape=(res, res))
_new_pressures = ti.var(dt=ti.f32, shape=(res, res))
_density_buffer = ti.var(dt=ti.f32, shape=(res, res))
_new_density_buffer = ti.var(dt=ti.f32, shape=(res, res))
color_buffer = ti.Vector(3, dt=ti.f32, shape=(res, res))
class TexPair:
def __init__(self, cur, nxt):
self.cur = cur
self.nxt = nxt
def swap(self):
self.cur, self.nxt = self.nxt, self.cur
velocities_pair = TexPair(_velocities, _new_velocities)
pressures_pair = TexPair(_pressures, _new_pressures)
density_pair = TexPair(_density_buffer, _new_density_buffer)
@ti.func
def sample(qf, u, v):
i, j = int(u), int(v)
# Nearest
rst = qf[max(0, min(res - 1, i)), max(0, min(res - 1, j))]
return rst
@ti.func
def lerp(vl, vr, frac):
# frac: [0.0, 1.0]
return vl + frac * (vr - vl)
@ti.func
def bilerp(vf, u, v):
s, t = u - 0.5, v - 0.5
# floor
iu, iv = int(s), int(t)
# fract
fu, fv = s - iu, t - iv
a = sample(vf, iu + 0.5, iv + 0.5)
b = sample(vf, iu + 1.5, iv + 0.5)
c = sample(vf, iu + 0.5, iv + 1.5)
d = sample(vf, iu + 1.5, iv + 1.5)
return lerp(lerp(a, b, fu), lerp(c, d, fu), fv)
@ti.kernel
def advect(vf: ti.template(), qf: ti.template(), new_qf: ti.template()):
for i, j in vf:
coord = ti.Vector([i, j]) + 0.5 - dt * vf[i, j]
new_qf[i, j] = bilerp(qf, coord[0], coord[1])
@ti.kernel
def apply_buoyancy(vf: ti.template(), df: ti.template(),
imp_data: ti.ext_arr()):
for i, j in vf:
v = vf[i, j]
den = df[i,j]
v[1] += (den * 25.0 - 5.0) * dt
# random disturbance
v[0] += (ti.random(ti.f32) - 0.5) * 80.0
v[1] += (ti.random(ti.f32) - 0.5) * 80.0
# velocity damping
den *= density_decay
v *= density_decay
vf[i, j] = v
df[i, j] = den
@ti.kernel
def curl(vf: ti.template()):
for i, j in vf:
vl = sample(vf, i - 1, j)[0]
vr = sample(vf, i + 1, j)[0]
vb = sample(vf, i, j - 1)[1]
vt = sample(vf, i, j + 1)[1]
velocity_curl[i, j] = (vr - vl + vb - vt) * half_inv_dx
@ti.kernel
def vorticity_confinement(vf: ti.template(), new_vf: ti.template()):
for i, j in vf:
force = ti.Vector([0.0, 0.0])
force[0] = (abs(velocity_curl[i+1,j]) - abs(velocity_curl[i-1,j])) * half_inv_dx
force[1] = (abs(velocity_curl[i,j+1]) - abs(velocity_curl[i,j-1])) * half_inv_dx
vc = velocity_curl[i, j]
force = vorticity * vc * force * ti.Vector([1.0, - 1.0]) / (force.norm()+1e-5)
new_vf[i, j] = vf[i, j] + dt * force
@ti.kernel
def divergence(vf: ti.template()):
for i, j in vf:
vl = sample(vf, i - 1, j)[0]
vr = sample(vf, i + 1, j)[0]
vb = sample(vf, i, j - 1)[1]
vt = sample(vf, i, j + 1)[1]
vc = sample(vf, i, j)
if i == 0:
vl = -vc[0]
if i == res - 1:
vr = -vc[0]
if j == 0:
vb = -vc[1]
if j == res - 1:
vt = -vc[1]
velocity_divs[i, j] = (vr - vl + vt - vb) * half_inv_dx
p_alpha = -dx * dx
@ti.kernel
def pressure_jacobi(pf: ti.template(), new_pf: ti.template()):
for i, j in pf:
pl = sample(pf, i - 1, j)
pr = sample(pf, i + 1, j)
pb = sample(pf, i, j - 1)
pt = sample(pf, i, j + 1)
div = velocity_divs[i, j]
new_pf[i, j] = (pl + pr + pb + pt + p_alpha * div) * 0.25
@ti.kernel
def subtract_gradient(vf: ti.template(), pf: ti.template()):
for i, j in vf:
pl = sample(pf, i - 1, j)
pr = sample(pf, i + 1, j)
pb = sample(pf, i, j - 1)
pt = sample(pf, i, j + 1)
v = sample(vf, i, j)
v = v - half_inv_dx * ti.Vector([pr - pl, pt - pb])
vf[i, j] = v
@ti.func
def smooth_step(a, b, x):
y = (x - a) / (b - a)
if y < 0.0:
y = 0.0
if y > 1.0:
y = 1.0
rst = (y * y * (3.0 - 2.0 * y))
return rst
@ti.kernel
def add_density(x: ti.i32, y: ti.i32, r: ti.i32, value: ti.f32):
for index in range((2*r+1)*(2*r+1)):
i = index // (2*r+1) - r
j = ti.mod(index, 2*r+1) - r
den = density_pair.cur[x+i, y+j] + value * smooth_step(r*r, 0.0, i*i + j*j)
density_pair.cur[x+i,y+j] = den
@ti.kernel
def fill_color_s(sf: ti.template()):
for i, j in sf:
s = ti.log(sf[i, j] * 0.25 + 1.0)
s3 = s * s * s
color_buffer[i, j] = ti.Vector([abs(1.5 * s), abs(1.5 * s3), abs(s3 * s3)])
def step(mouse_data):
# advection
advect(velocities_pair.cur, velocities_pair.cur, velocities_pair.nxt)
advect(velocities_pair.cur, density_pair.cur, density_pair.nxt)
velocities_pair.swap()
density_pair.swap()
# add density to density field
add_density(int(res * 0.25), 50, 25, 0.8)
add_density(int(res * 0.75), 50, 25, 0.8)
if mouse_data[2] > 1.0:
add_density(int(mouse_data[0]), int(mouse_data[1]), 25, 0.9)
# apply buoyancy
apply_buoyancy(velocities_pair.cur, density_pair.cur, mouse_data)
# vorticity confinement
curl(velocities_pair.cur)
vorticity_confinement(velocities_pair.cur, velocities_pair.nxt)
velocities_pair.swap()
# pressure projection
divergence(velocities_pair.cur)
for _ in range(p_jacobi_iters):
pressure_jacobi(pressures_pair.cur, pressures_pair.nxt)
pressures_pair.swap()
subtract_gradient(velocities_pair.cur, pressures_pair.cur)
fill_color_s(density_pair.cur)
def vec2_npf32(m):
return np.array([m[0], m[1]], dtype=np.float32)
class MouseDataGen(object):
def __call__(self, gui):
# [2:4]: current mouse xy
mouse_data = np.array([0] * 3, dtype=np.float32)
if gui.is_pressed(ti.GUI.LMB):
mxy = vec2_npf32(gui.get_cursor_pos()) * res
mouse_data[0], mouse_data[1] = mxy[0], mxy[1]
mouse_data[2] = 2.0
else:
mouse_data[2] = 0.0
return mouse_data
def main():
global debug
gui = ti.GUI('Smoke-Fluid', (res, res))
md_gen = MouseDataGen()
paused = False
while True:
while gui.get_event(ti.GUI.PRESS):
e = gui.event
if e.key == ti.GUI.ESCAPE:
exit(0)
mouse_data = md_gen(gui)
step(mouse_data)
img = color_buffer.to_numpy()
gui.set_image(img)
gui.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()